How long do car batteries last
The answer to how long car batteries lasts
People always ask how long car batteries last. The answer is: 3-4 years. If you try to squeeze more life out of yours, at least have your battery tested every six months or buy your own battery tester (see below). The Batteries Council International’s study “Failure modes from batteries removed from service,” demonstrates that a typical car battery now last 55-months in 2010, compared to just 34-months in 1962.
Heat and corrosion are the #1 reasons car batteries die
The kind of battery terminal corrosion in this  photo is not the norm. A battery terminal can look just fine, yet be almost 90% non-conductive. In those cases the battery can start the vehicle fine one day and be dead as a door nail the next morning.
photo is not the norm. A battery terminal can look just fine, yet be almost 90% non-conductive. In those cases the battery can start the vehicle fine one day and be dead as a door nail the next morning.
In fact, that type of go/no-go situation happens often during seasonal changes where underhood temperatures can be around 140° while running, and overnight temperatures can dip down to 30ۥ or less. The temperature extremes cause expansion and contraction at the battery terminals, allowing more corrosion and high voltage drops. So clean your battery terminals by providing backup power, removing the terminals and cleaning with a battery wire brush, and applying a dielectric grease to the battery post. But follow this procedure before disconnecting the battery terminals.
Heat affects how long car batteries last
Most car owners think that cold weather kills batteries. While batteries fail often in cold weather, they were most likely poisoned in warm weather. Read this statement from Bill Darden, author of batteryfaq.org
“Even though battery capacity at high temperatures is higher, battery life is shortened. Battery capacity is reduced by 50% at -22 degrees F – but battery LIFE increases by about 60%. Battery life is reduced at higher temperatures – for every 15 degrees F over 77, battery life is cut in half. This holds true for ANY type of Lead-Acid battery, whether sealed, gelled, AGM, industrial or whatever.”
High heat is the reason many car makers install a battery insulator around car batteries stored under the hood. And, its one of the reasons car makers are moving the battery to other locations in the vehicle.
Maintenance free batteries shouldn’t need water
Today’s batteries are maintenance free, so they don’t need
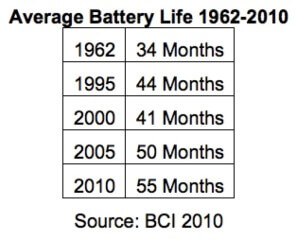
Increased life expectancy of car batteries over the years
regular doses of water to maintain electrolyte levels and the terminals are sealed better, so they don’t corrode as often. That’s the good news. The bad news is that today’s batteries are far more sensitive to abuse and today’s cars place more electrical demands on the vehicle’s electrical system. If you drain a modern battery by leaving your lights on, you’re far more likely to cause permanent damage to the plates, preventing the battery from recovering fully after recharging. Or, if you idle long periods in stop and go traffic while running your AC and blower, high powered music system, navigation system, electric seats and mirrors, your car can’t generate enough power to run all those accessories so that power has to come from the battery.
What happens to a car battery when you leave your lights on?
Today’s cars have far more electronics than car from the ‘60’s. Power hungry options like heated seats, rear window defoggers, and “always-on” computers can drain a battery quickly if you drive short distances.
And it’s not just the electrical devices in your car. To make a maintenance free battery, manufacturer’s had to alter the materials used in the plate grid. First, the manufacturers had to reduce the amount of “gassing” that occurred during recharging because that led to water loss. So they replaced the Antimony in plates with Calcium. Calcium reduced gassing and water loss by 80%. And Calcium reduced the self-discharge that normally occurs in a “wet cell,” even when there’s no current draw.
The downside to adding Calcium comes during recharge. With Antimony, the high gassing agitated the acid during recharge and actually helped mix the acid. Without that high level of gassing, the acid becomes stratified. So the acid weight can be 1.17 near the top of the plate and 1.35 near the bottom. That leads to sulphation and grid corrosion, causing underused capacity and premature failure.
Car batteries lose power when sitting
A car battery is a “wet cell” and it loses a 1-2% of its charge every day, even with no current draw on it. The amount of self discharge depends on the ambient temperature. A warmer ambient temperature results in more chemical activity in the battery and faster self-discharge.
Computers drain car batteries all the time
Every modern vehicle draws power from the battery even when the engine is off. The main computer draws about 50 milliamps at all times. This “keep alive” memory maintains all the “learned values” in the computer. In addition to learning the changes your engine and transmission have undergone since the day it came off the factory floor, the computer also retains the learned values from your anti-pinch windows, closed throttle, power sliding doors, HVAC actuators, and security system. Once you lose battery power, your vehicle forgets those values. When you replace the battery, the computer can relearn some values on its own. But others must go through a “re-learn” process conducted by a technician using a scan tool. That’ll cost you at least $125. So it’s really important that you don’t let your battery get to the point of complete failure.
Never let you car sit for more than 30-days without starting
A typical battery will discharge enough in 30 days due to self discharge and computer draw that battery voltage can drop to the point where the computer forgets its learned values. Starting the car and letting it idle will NOT recharge the battery enough to replace the lost power. In fact, starting and idling does more harm than good because it can’t even replace the power used to start the engine, let alone replace the charge lost due to parasitic load. If you don’t plan to drive your car for more than a week, either attach a battery maintainer, or have someone drive it AT HIGHWAY SPEED every two weeks for at least 15-mins.
Symptoms a car battery is about to fail
Before a car battery fails it sends out warning signals. If you ignore them, prepare to be stranded some day.
• Your headlights dim while idling,
• Your blower motor slows down when idling.
• The engine cranks slowly first thing in the morning.
The problem can be a dying battery or a weak alternator. Either way, you must take action and have the battery and charging system tested. Don’t ignore these symptoms! The root problem may be something as simple as corrosion at the terminals. If left uncorrected, the voltage drop can result deep battery discharge and excessive heat loads for the alternator, causing it to fail. At that point you’ve turned a $25 terminal cleaning job into a $600 repair bill for a new battery and alternator.
© 2013 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat
