How to adjust a manual belt tensioner
How to adjust a manual belt tensioner to get the proper belt tension
DIYers tend to over-tighten drive belts and that can cause premature wear on the driven component’s bearings. I’ll show you how to adjust a manual belt tensioner to get just the right amount of belt tension.
First, check the condition of any idler rollers in the drive system
The bearing in the tensioner idler roller is a wear item  and should be replaced at the same time as the belt.
and should be replaced at the same time as the belt.
Move the component or pulley to tighten the belt as you push on the middle section
Tighten a belt tensioner by turning the long adjustment bolt while pushing on the middle of the belt. You want just a 1/2″ movement. Any less than that and the belt is too tight. If you have more than 1/2″ movement, the belt is too loose.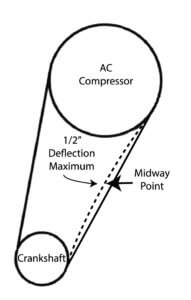
Once you have the 1/2″ deflection, tighten the tensioner locking bolt.
Start the engine and run for 3 to 5 minutes to seat the belt in the pulley grooves. Then check belt tension again and adjust belt tension again.
What happens if the drive belt is too tight?
A drive belt that’s too tight puts added stress on the driven component’s bearing, causing them to fail early.
A drive belt that’s too tight can also make a “twanging noise,” almost as if it’s be plucked like a guitar string.
What happens if the drive belt is too loose?
The belt will slip and squeal on cold start, causing it to glaze and make even more noise as it continues to slip on the pulleys.
Can you tighten an automatic tensioner?
No. The spring in the automatic tensioner is calibrated to provide the correct tension for the belt. However, as auto tensioners wear out, the spring can
rust and degrade and the dampening mechanism in the tensioner can also wear. A rusted spring can bind and cause a tighten/release result that allows the belt to slip.
A worn dampening mechanism causes the belt to transfer engine power pulses to the belt, resulting in belt vibration, noise and premature component wear.
If you have an automatic belt tensioner, replace it when you replace the belt
Modern EPDM drive belts have an average life of around 100K miles and the tensioner has the same life. Replace the belt and tensioner together.
©, Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat

