Cold cranking amps — What are they and how many do you need
Cold cranking amps is a measure of how much cranking power a battery can deliver in cold weather
To properly rate a battery’s starting ability in cold weather, you have to test it at an industry defined temperature, for an industry defined time period, with an industry defined maximum drop in voltage; cold cranking amps (CCA). The more CCAs, the more power it will have to crank a cold engine. Here’s how CCA are measured
CCA test routine
Cranking amps (CA) refers to the number of amps a battery can output at 0°F (-17.8°C) for 30-seconds while still maintaining at least 7.2 volts. All car batteries are rated in CCA and reserve capacity. However, some jumper packs rate their products in peak amps. There is no industry recognized standard for measuring peak amps, so it’s a meaningless term and can’t be used to judge how capable the battery will be in starting an engine.
How many cold cranking amps does your car need?
All carmakers list the minimum CCA in the owner’s manual. You can buy a car battery with more CCA than the carmaker recommends, but you should never buy a battery with less than the recommended amount.
As a general rule, you need 1 Cold Cranking Amp for every cubic inch of engine displacement (2 CCA for diesel engines).
How to read a car battery’s rating
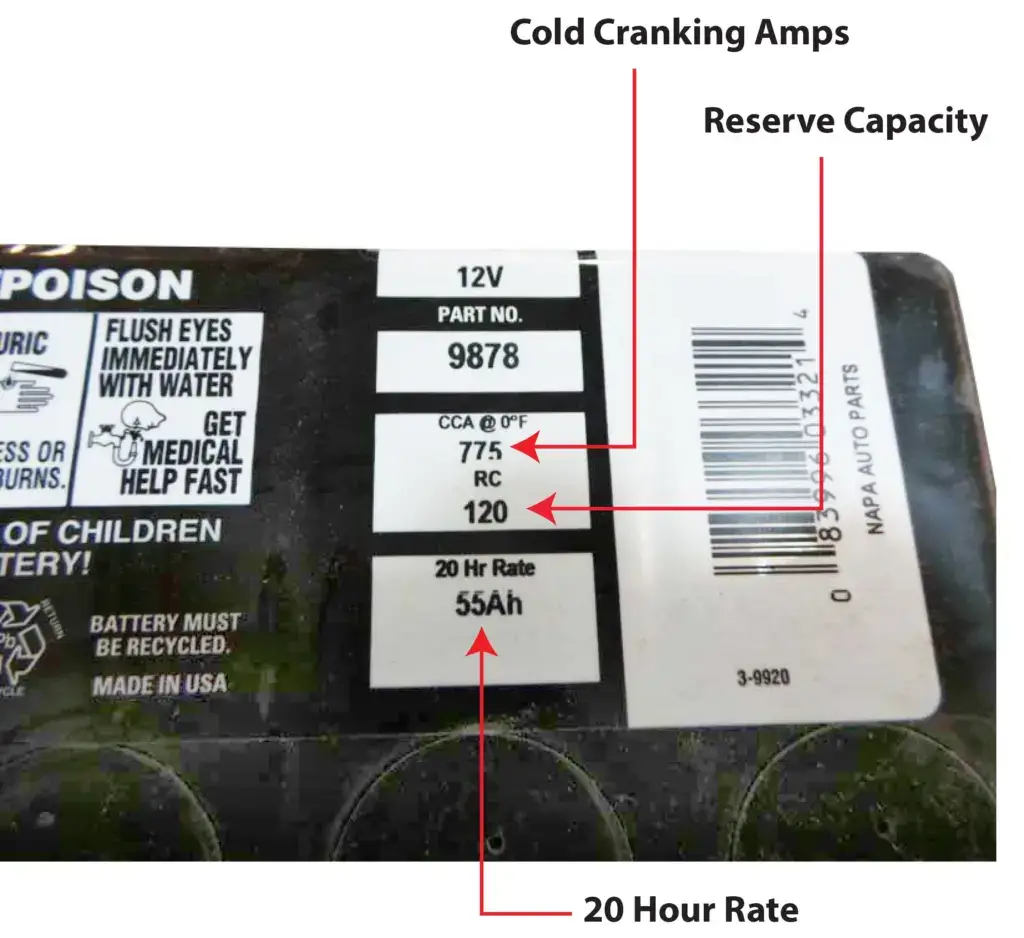
CCA — Listed above
Reserve Capacity (RC)
Reserve capacity is a measure of the amount of time a battery can continuously supply power to a vehicle’s electrical system in the event of a charging system failure or when the engine is turned off. It is measured in minutes and is more important these days because of parasitic drain, which is the battery energy that’s used when the key is off.
The reserve capacity of a battery is measured in minutes and at a temperature of 80°F. For example, if the RC or reserve capacity rating is rated at 80, the battery can provide 25 amperes for 80 minutes before losing its power.
The reserve capacity of a battery is determined by the amount of lead plates and electrolyte solution inside the battery. The more lead plates and electrolyte solution, the higher the reserve capacity. A standard reserve capacity for a car battery is usually around 45 to 60 Ah.
Amp-Hours
A battery’s amp-hour rating tells you how much power you car draw from the battery and for how long. In other words, it’s unit of measure for a battery’s electrical storage capacity. It’s calculated by multiplying the current in amperes by the time it takes to discharge the battery. For example; a battery that delivers 5 amperes for 20 hours delivers 5 amperes x 20 hours = 100 amp-hrs of capacity.
20 Hour Rate
For deep cycle batteries the standard rating is 20 hours. So, if a battery has a rating of 100AH @ 20Hr rate, then that battery was discharged over 20 hours with a 5 amp load. However, starting batteries are typically rated at the 10Hr rate. It’s unusual to see a starting battery listed with a 20 hour rate.
Is it better to buy a battery with more CCA than the factory battery?
Not always. Batteries are designed in group sizes, so if your car requires a Group 34 battery, it’s a standard height, width, and depth. In order to get more CCAs out of a Group 34 battery, the manufacturer must use different style lead plates and most often they’re thinner to allow for more contact with the electrolyte. That plate design may produce more CCAs but at the expense of reserve capacity. In other words, there’s no free lunch.
©, 2020 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat