Ignition Coil Circuit Malfunction Code: What it means
Learn what an Ignition Coil Circuit Malfunction Code Means and how to fix the problem
An Ignition Coil Circuit Malfunction is usually listed as codes P0350 through P0362. These codes indicate that the ECM has detected that the coil isn’t operating properly. The ECM can’t detect whether the problem is in the primary or secondary circuit.
P0350 Ignition Coil Primary/Secondary Circuit Malfunction
P0351 Ignition Coil A Primary/Secondary
P0352 Ignition Coil B Primary/Secondary
P0353 Ignition Coil C Primary/Secondary
P0354 Ignition Coil D Primary/Secondary
P0355 Ignition Coil E Primary/Secondary
P0356 Ignition Coil F Primary/Secondary
P0357 Ignition Coil G Primary/Secondary
P0358 Ignition Coil H Primary/Secondary
P0359 Ignition Coil I Primary/Secondary
P0360 Ignition Coil J Primary/Secondary
P0361 Ignition Coil K Primary/Secondary
P0362 Ignition Coil L Primary/Secondary
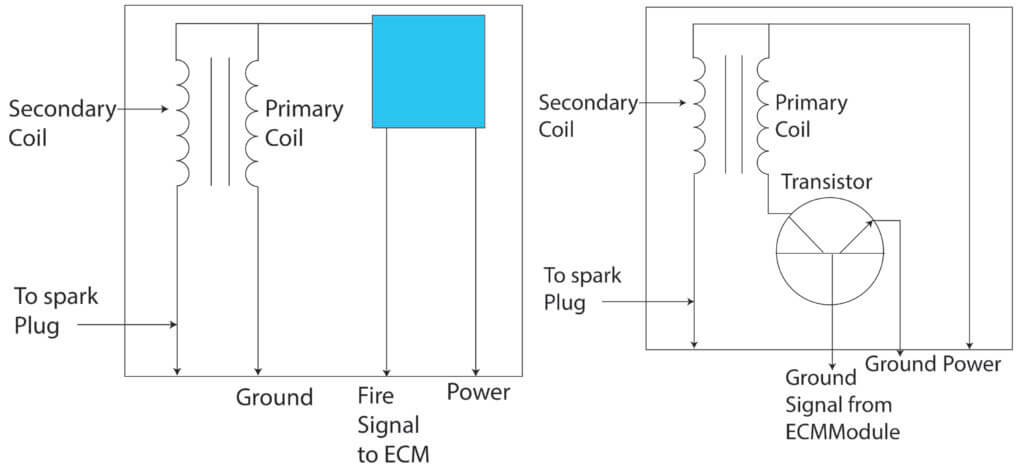
Carmakers can label the coils by their cylinder number or by a letter. In many cases, the ECM or the ignition module provides ground to the primary circuit of each ignition coil when it wants to build a magnetic field. Then, it turns off the ground circuit when it wants the coil to fire. The magnetic field collapses, and the firing voltage is just 25,000 to 40,000 volts to fire the spark plug.
What causes an Ignition Coil Circuit Malfunction?
Power comes to the primary side of the coil from the ignition switch (on older vehicles), the ignition control module, or the relay in the smart power distribution box. The ECM or ignition module provides the ground to the primary circuit. If it doesn’t see voltage on the ground side of the primary coil circuit, it will set this code. The problem can be a blown fuse, bad relay, bad module, wiring harness issue, or bad connector. Start by checking for power to the primary side of the ignition coils to diagnose this problem. The code definitions above tell you which coil is causing the problem.
In addition, on some late-model vehicles with coil-on-plug ignition systems, several carmakers have added a solid-state sensor to detect if and when the secondary coil fires. If the coil doesn’t fire, the ECM will also set this code.
Understanding the primary and secondary circuits of an ignition coil
Each ignition coil is built with two bobbins of wire. The primary coil has 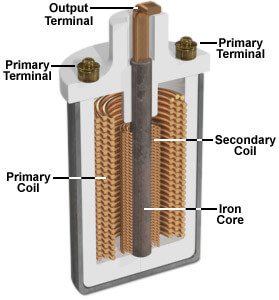 thicker but fewer windings than the secondary coil. When the primary coil is powered up, an electrical field is induced into the secondary coil. When the primary current is shut off, the electrical field collapses.
thicker but fewer windings than the secondary coil. When the primary coil is powered up, an electrical field is induced into the secondary coil. When the primary current is shut off, the electrical field collapses.
Because the secondary has so many more windings, it converts the electrical field into very high voltage. That voltage travels down the ignition wire and jumps the spark plug gap, igniting the air-fuel mixture.
These trouble codes indicate a problem with either the primary or secondary circuits. Coil A is the coil for the #1 spark plug.
© 2012 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat