How Active Wheel Speed Sensors Work
Active wheel speed sensors; how they work and how they differ from passive wheel speed sensors
An active wheel speed sensor detects the presence of a magnetic field and reports that presence as a square wave DC digital on/off signal, as opposed to a passive wheel speed sensor which produces an analog AC signal. When used in an anti-lock brake system, an active sensor detects the alternating the north/south poles of a rotating multipole magnetic ring, usually inserted into the wheel bearing.
As the wheel rotates, the active wheel speed sensor detects the pole switching and sends a digital on/off signal to the ABS control module.
An active wheel speed uses a Hall Effect Sensor and requires power
The active sensor receives a 12v power supply from the electronic brake control module and provides an output signal to the brake control module. As the wheel spins, the wheel speed sensor sends a DC square wave signal. The brake control module uses the frequency of the square wave signal to calculate the wheel speed.”
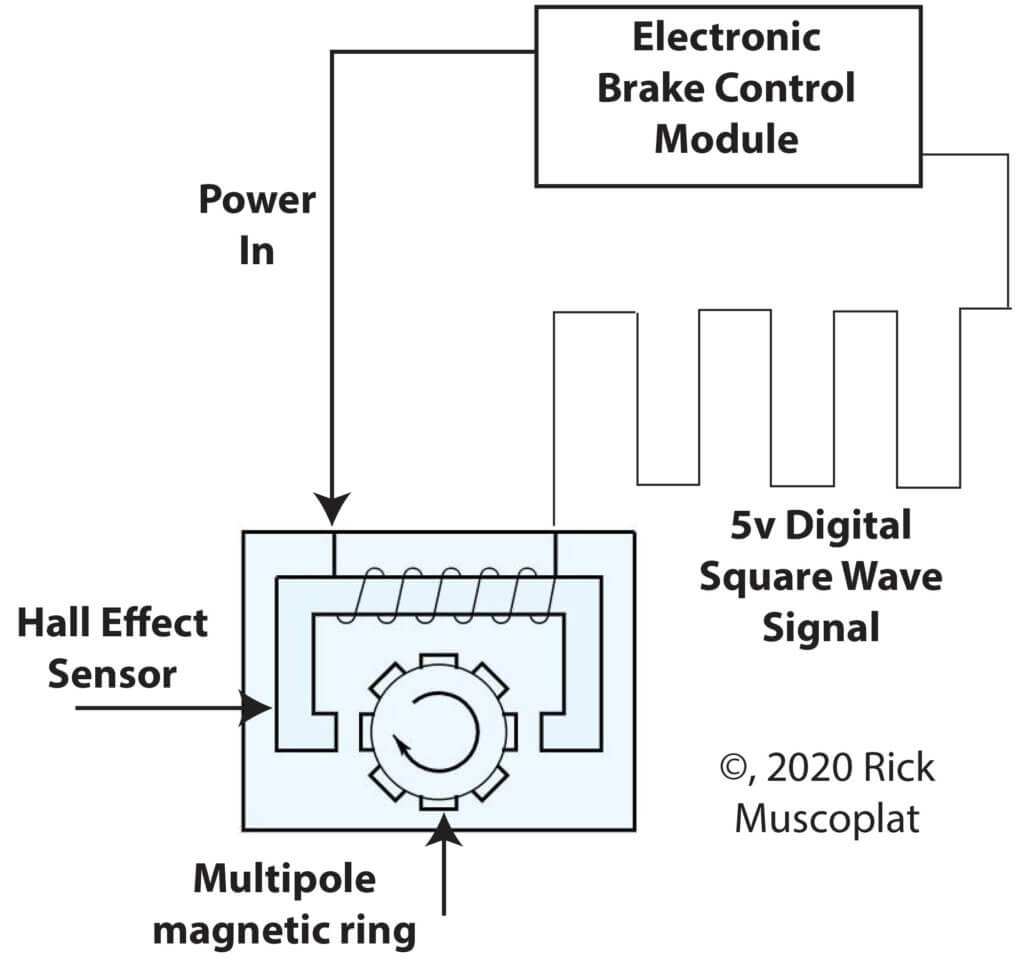
The brake control modules provide power to the Hall Effect Sesnor which reacts with the rotating multi-pole magnetic ring on the wheel bearing. The brake control module gets a digital signal.
How does an active sensor differ from a passive sensor?
An active wheel speed sensor requires power, while a passive wheel speed sensor generates its own AC power with wheel rotation.
A passive sensor includes a wire wrapped magnet that generates a low AC voltage as a steel toothed ring passes by the sensor.
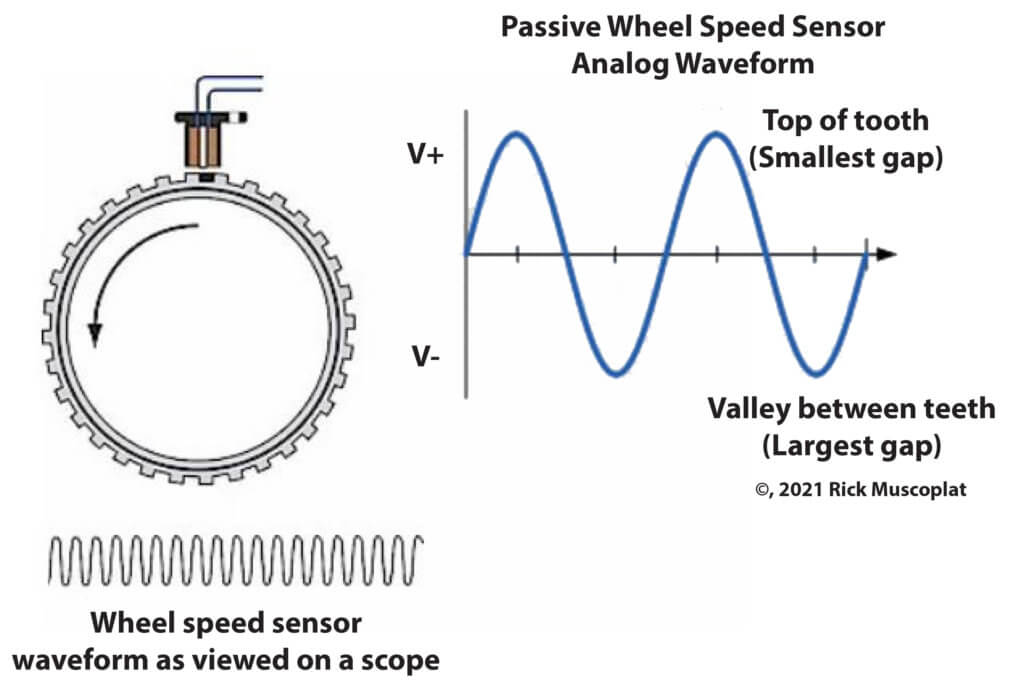
A passive wheel speed sensor generates a sine wave pattern
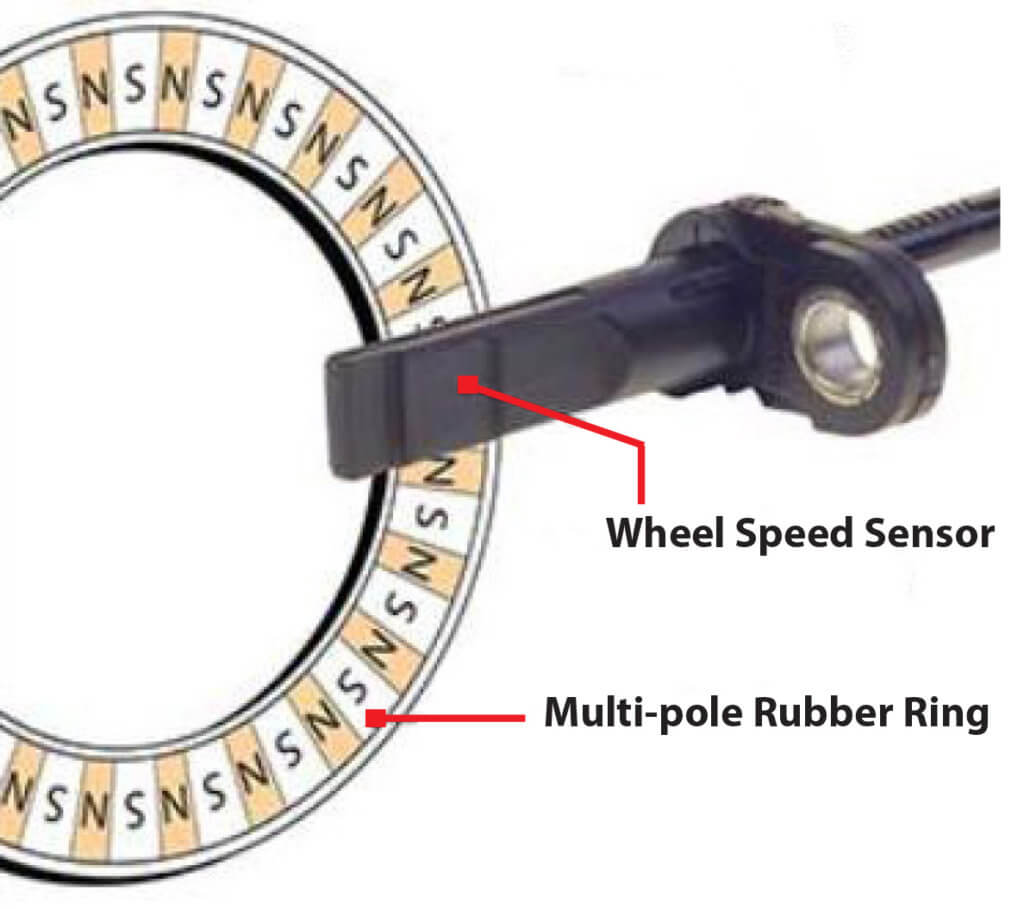
Notice the alternating magnetic fields of the multipole ring. The sensor reads the alternating magnetic fields
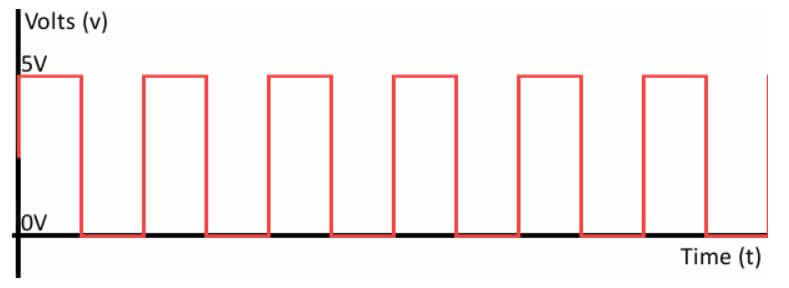
Digital wheel speed signal
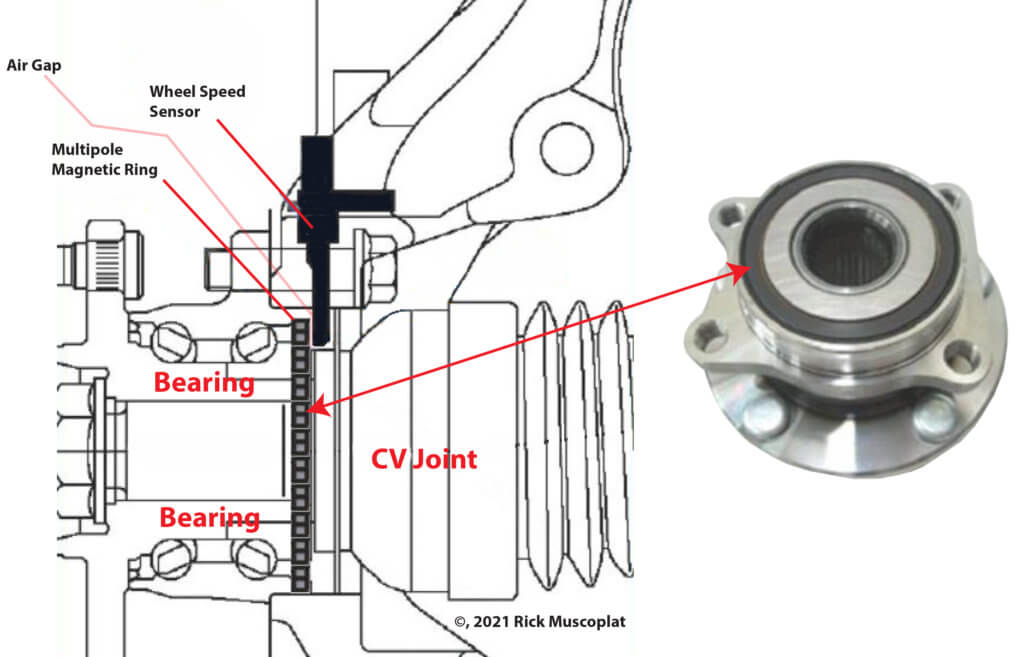
Notice the black ring on the wheel bearing. That’s the multipole magnetic ring
For more information see the video on the BCA bearings site
©, 2021 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat