Oil filter for synthetic oil
Best oil filter for synthetic oil
Most late model engines require synthetic oil because it lasts longer and provides better protection against engine wear. So carmakers now recommend longer intervals between oil changes. But oil life depends on many factors, including: how you drive (short trips, stop and go traffic versus longer trips at highway speeds), load factors such as towing, long periods of idling, how long the engine sits idle (oil accumulates contaminates like acids and water which causes sludge and corrosion), and the type of oil filter you use. If you use the recommended synthetic oil and change it according to the carmakers’ recommendations but use a cheap oil filter that’s not designed for synthetic oil, you’re not getting all the benefits of synthetic oil. So, what makes an oil filter for synthetic oil different from other filters? Here’s what to know about how to buy the best oil filter for synthetic oil.
What the oil filter does
As oil racks up the miles, it picks up carbon (soot from blow-by gasses), water from gasoline combustion, and acid byproducts from combustion. When mixed together and churned with air, the components oxidize and form a black gooey sludge-like substance. The oil filter’s job is to capture and hold these contaminants. However, if the filter media reaches its limit, where it can no longer filter the oil, its bypass valve will open and your engine’s oil will simply bypass the filter and continue to carry the contaminates throughout your engine.
Oil tear-down tests are meaningless
Lots of wanna-be engineers post spin-on filter tear-down tests on YouTube. The tests prove absolutely nothing because you can’t judge a filter visually. Let’s look at what these tear-down tests measure and examine why they’re irrelevant to judging the filter’s effectiveness or projected lifespan.
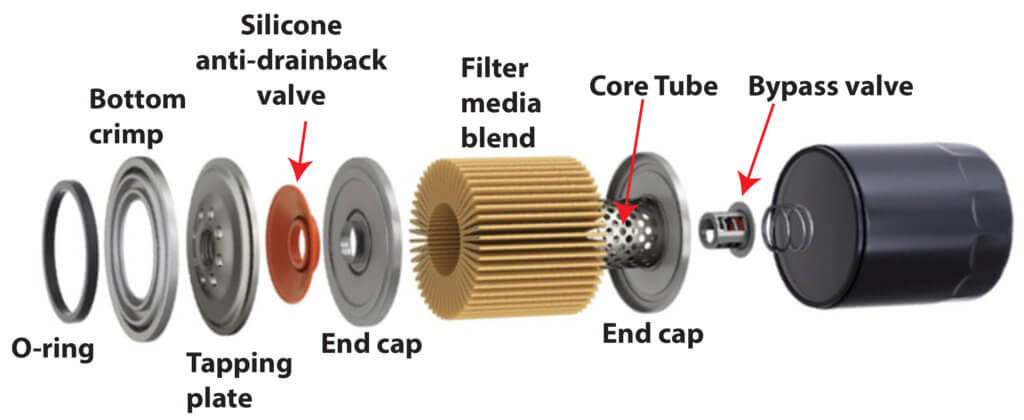
Oil filter Tapping plate thickness
Some tear-down tests measure the gauge of the tapping plate (the part that screws onto the engine). Tapping plate thickness is a total red herring. The plate only needs to be thick enough to not deflect when properly torqued to the filter mating surface. A thicker doesn’t extend the life of the filter or improve its performance. As long as the tapping plate doesn’t deflect, it’s doing its job.
Filter media dimensions and pleat count
There are well over 80 different types of filtration media used in modern oil filters. It’s the filtering media’s efficiency that counts, not total square inches or pleat count. In fact, a smaller size high efficiency filter media can outperform a much larger sheet of low efficiency filter media. Unless you know the filter media material construction and its efficiency rating, measuring its size or pleat count is a complete waste of time. Those specifications provide no meaningful data on which to judge the filter.
End cap construction
In a spin-on filter, the job of the end cap is to prevent the oil from bypassing around the ends of the pleats. Some filter manufactures use metal end caps filled with adhesive resin. In those designs, the pleats are inserted into the molten resin-filled caps and the adhesive is cured. Other designs use resin-impregnated fiber board that’s then coated with adhesive before mating with the pleats. Both designs are equally effective because, again, the end caps’ job is to retain the pleats and prevent oil from bypassing around the pleats. As long as the resin adhesive holds the pleats, the cap is doing its job. In other words, it’s the quality of the adhesive resin that counts, not what the cap itself is made of.
Oil filter Core tube
The core tube prevents clogged pleats from collapsing into the center of the filter. As long as the core tube provides a consistently rigid surface area along the backside of the pleats, the actual material is irrelevant.
Oil filter Anti-drainback valve
When the oil filter is mount on the top or side of the engine, oil can leak out of the filter when the engine is off, causing a delay in building oil pressure on the next start. So filter manufactures often install a rubber-like seal to prevent the oil from leaking out of the filter. Inexpensive filters use neoprene while the more expensive filters use silicone. Neoprene hardens and cracks with heat and age while silicone maintains its elasticity throughout the filter’s life.
What wears out the oil filter components?
• Viscosity Improver (VI) breakdown. All multi-viscosity oils contain VI. They’re polymers that uncoil as they heat to reduce oil thinning (or, as most people think; “thicken” the oil). Shear stress cuts the polymers, reducing the oil’s resistance to thinning. The longer you run the oil, the more you shear the VI. So longer oil change intervals tend to clog conventional filters with degraded VI.
• Acid. Acids degrade the plastic and neoprene/silicone components used in the bypass and anti-drain back valves. They also attack the end cap resin, weakening the adhesive and allowing oil to bypass around the pleats. This can happen with both metal end caps as well as resin impregnated end caps. In other words, the quality of the bonding resin and it’s resistance to chemical degradation is far more important than the end cap material.
• Carbon, water and sludge. All engines
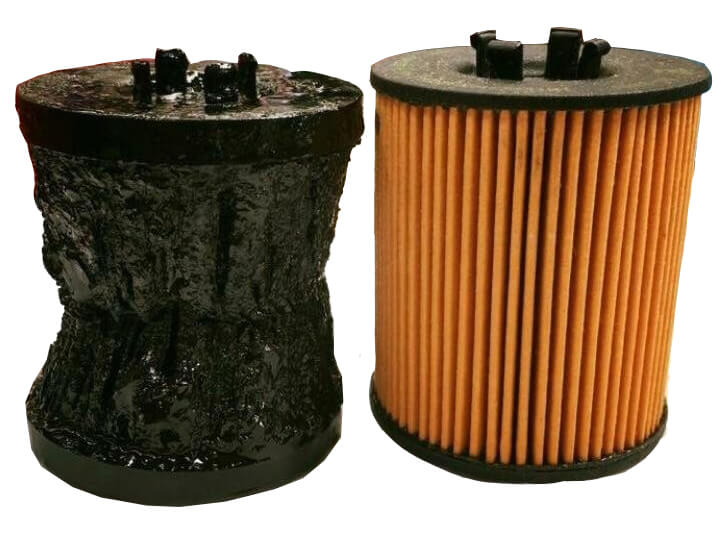

Sludge buildup and collapsed pleats
have blow-by, but worn engines have much more blow-by. In addition, cold starts and short trips add considerably more carbon and water to the oil, which creates more sludge. Sludge clogs the oil filter much faster than particulate matter.
How to choose the best oil filter for synthetic oil
Read the numbers. It’s all about efficiency, not dirt holding capacity
An oil filter’s efficiency rating is important to judging its quality. An oil filter’s micron rating refers to the smallest particle the filter media can capture and hold.
An oil filter’s “efficiency rating” is the filter’s ability to capture and hold a maximum percentage of a certain particle size. So a filter with a 98% efficiency rating and micron size of 20-microns will filter out 98% of all particles 20-microns and larger.
Oil filter dirt holding capacity
Some oil filters list its dirt holding capacity, usually listed in grams. But unless you know the filter’s efficiency rating and micron size, dirt holding capacity is a meaningless number.
Choose a filter with blended media
Oil filters capture small particles by trapping them in very small pores. But what about the liquid contaminates in oil like acids and water? Those can flow right through the pores of conventional filter materials. Synthetic glass fibers, on the other hand, attract liquids using surface tension. Several high end oil filters for synthetic oil are a blend of high efficiency cellulose materials blended with synthetic fibers.
Silicone anti-drainback valve
The best filters for synthetic oil have silicone anti-drain back and bypass valves.
©, 2021 /Rick Muscoplat
