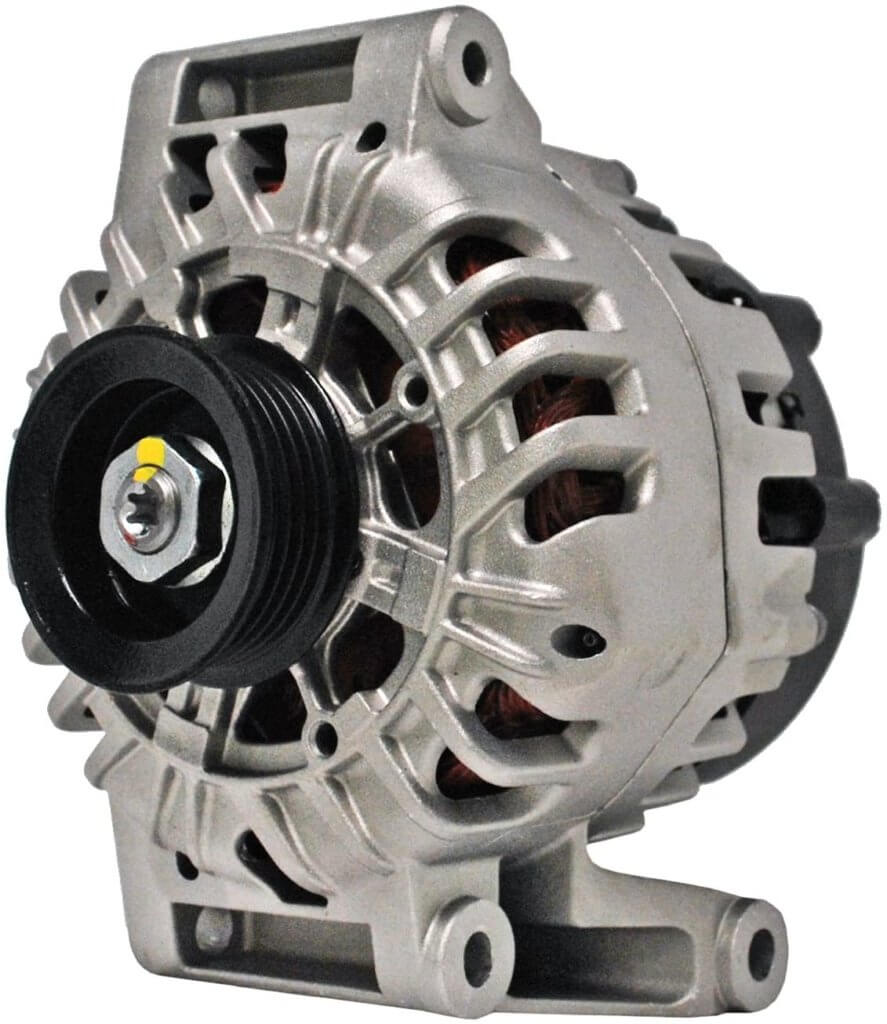
What is an Alternator in a Car and How Does it Work?
An alternator is an AC generator and is used to provide power to the engine, transmission, and all your electrical accessories
The alternator in a car provides electrical power to recharge the battery
and to provide additional electrical current to power high-draw electrical accessories like heated seats, window defoggers, blower motor, etc.
How does a car alternator work?
In simple terms, an alternator produces electricity by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy. Most car alternators are driven by a belt that’s connected to the engine’s crankshaft. The belt spins an electromagnet called a rotor. A series of electrical windings called a stator surround the rotor. As the electromagnet spins, the magnetic field produces electron movement in the stator windings. That electron movement is electricity.
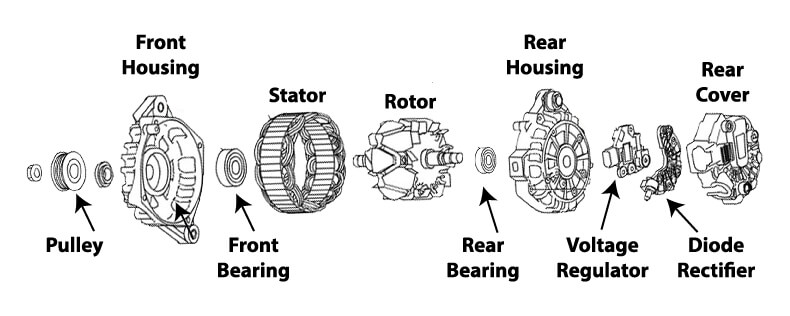
Exploded view of car alternator showing voltage regulator, diode rectifier, front and rear alternator bearings, alternator rotor and stator, and housings
The rotor has a North and South pole, so as it spins, it moves electrons in one direction as the North pole passes and then in the opposite direction as the South pole passes. This is what produces alternating current (AC). Since vehicles operate off of direct current, diodes (one-way electrical valves) convert the AC current into DC current.
Alternator output is directly related to engine RPM
The alternator has a smaller pulley than the crankshaft pulley, so it rotates at approximately 3 times the speed of the engine. In other words, at 2,000 engine RPM, the alternator spins at 6,000 RPM.
However, because the alternator speed is directly related to engine RPM, its output varies with engine speed. An alternator that’s rated at 140-amps, can only output that rating when the engine RPM is at or above 2,000. When the engine is at idle speed (around 600-RPM), the alternator output drops to less than 40 amps.
What causes alternator failure?
An alternator can have a mechanical failure
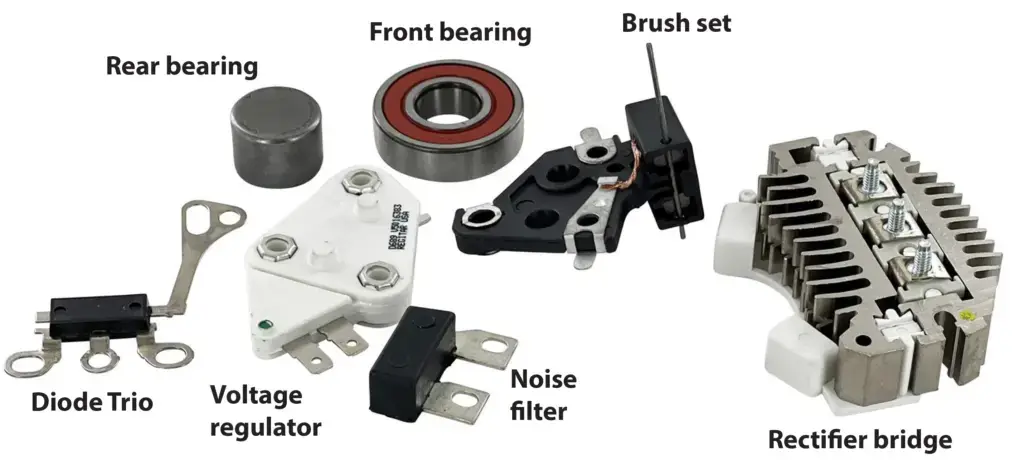
A car alternator has mechanical components: pulley, front and rear bearings, brushes and slip rings that can wear and fail. All mechanical components are subject to wear over time. The brushes that ride on the slip rings can wear out and cause total or intermittent failure. A bearing failure can cause the rotor to contact and destroy the stator windings.
Extreme vibration can also cause mechanical components to fail. A worn harmonic balancer, or worn automatic belt tensioner can cause vibration in the drive belt system that transfers to the alternator bearings, accelerating wear and causing pre-mature failure.
But electrical component failures are the most common cause of alternator failures
An alternator’s rotor windings, stator windings, diodes, and rectifiers, and in some cases a voltage regulator can fail, causing an alternator to stop producing power. The most common cause of electrical component failure is excessive heat.
What causes excessive alternator heat?
High underhood temperatures degrade insulation on the rotor and stator windings
Using your alternator to recharge a dead battery can cause excessive diode and rectifier heating that can cause premature failure.
©, 2023 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat


