2013 3.5L Firing Order
Learn the firing order and specs for the 2013 Ford 3.5L engine
This article contains the 2013 Ford 3.5 engine firing order along with engine and tune-up specifications.
In Ford offered three versions of the 3.5-liter engine.
VIN B is 3.5L, 213 cubic inches, Sequential multi-port fuel injection, with 285 horsepower. VIN B is naturally aspirated with dual overhead cam and 4 valves per cylinder. It is used on the Edge, Flex, Taurus, Lincoln MKX, MKS, and MKT models.
VIN C is a 3.5L, 213 213 cubic inches, Sequential fuel injection with 285 horsepower. VIN C is part of Ford’s Cyclone family. It is naturally aspirated with a single overhead cam and 2 valves per cylinder. It was used on the Freestar and Monterey Minivans and the Freestyle crossover
VIN T is a 3.5L, 213 213 cubic inches Gasoline Direct Injection that outputs 365 horsepower. VIN T is part of Ford’s Ecoboost family. It is twin-turbocharged with dual overhead cams and 4 valves per cylinder. It was used on the F150, Expedition and Navigator SUVs, Explorer, Flex, Taurus, MKS, MKT, and MKX vehicles.
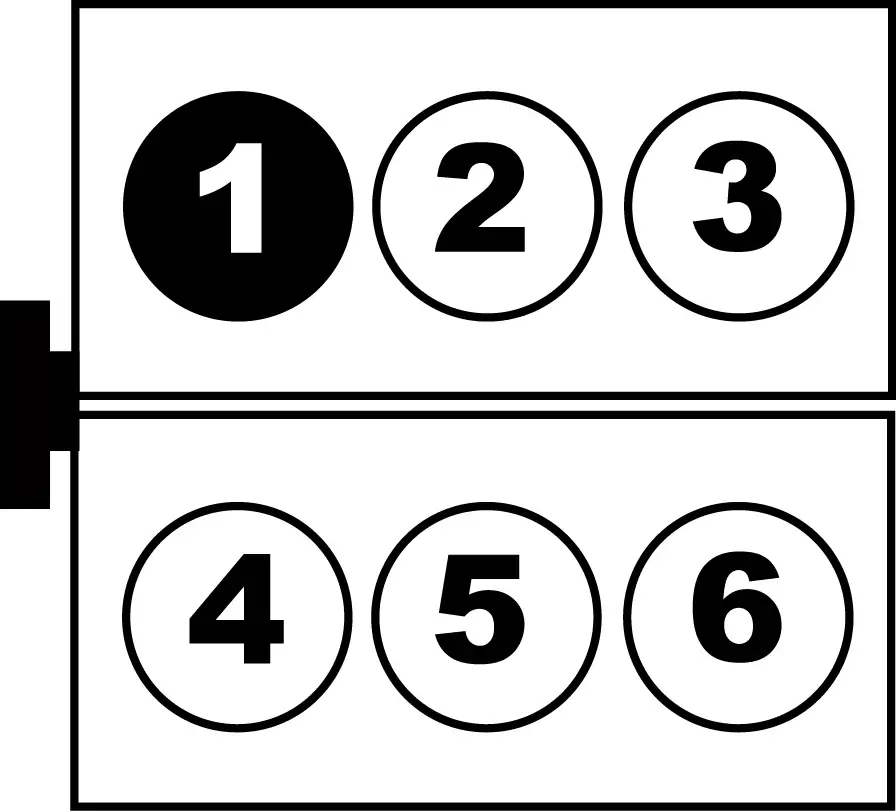
2013 Ford Explorer 3.5 Firing Order and engine layout
Firing Order 1-4-2-5-3-6
Platinum MOTORCRAFT SP520
Spark Plug Gap
0.051″
Spark Plug Torque Setting
133 in/lb
Coil on Plug torque setting
62 in/lb
2013 Ford Explorer 3.5L non-turbo fuel pressure specifications
Engine running 55 psi
Key ON Engine OFF 58 psi
2013 Ford Explorer 3.5L non-turbo valve adjustment specifications
Intake: 0.15 mm (0.0059 in) – 0.25 mm (0.0098 in)
Exhaust: 0.36 mm (0.0142 in) – 0.46 mm (0.0181 in)
Ford 2013 3.5L Engine Construction and specifications
This 3.5-liter V6 is a natural aspirated gasoline engine non-turbo. It is referred to as a Cyclone engine
Engine block: Cast Aluminum allow, open-deck type, cast-in liners,
Crankshaft: Forged crankshaft (4130 alloy steel), securely hold by 6-bolt billet steel main caps.
Pistons: Lightweight, low-friction aluminum pistons. Additional cast-in oil squirters inside the engine to spray engine oil on bottom ends of pistons.
Cylinder head: Aluminum with four valves per cylinder. Mechanical buckets. Chain-driven double overhead camshafts (DOHC) with variable intake timing (iVCT) or variable intake and exhaust timing (Ti-VCT – twin-independent variable cam timing).
Water pump:Chain-driven water pump at the front, under a front-end engine cover.
Fuel: Electronically controlled sequential multi-port fuel injection and coil-on-plugs type ignition.
©, 2023 Rick Muscoplat