What’s the difference between an intercooler and a radiator
Intercoolers and radiators look alike but they perform different jobs.
An intercooler and a radiator are both heat exchangers but one cools air and the other cools antifreeze
A radiator is a heat exchanger that removes heat from engine coolant
A radiator sits right behind the grille. As air passes through the radiator, it picks up heat from the engine coolant, reducing the temperature of the coolant inside the radiator. In other words, a radiator is designed to cool engine coolant. The air coming out of the backside of the radiator is superheated and exits the engine compartment from the underside of the engine.
An intercooler removes heat from air that was heated by the turbocharger or supercharger
An intercooler is used on engine with either a turbocharger or supercharger. Superchargers and turbochargers compress air and push it into the cylinder to gain put more oxygen molecules into every air/fuel charge. However, the process of compressing air causes it to heat up, requiring cooling before it enters the cylinder. An intercooler is between the the turbocharger or supercharger and the intake manifold. It’s job is to pass outside air across the fins of the intercooler to remove heat from the compressed air.
Differences in construction between an intercooler and a radiator
Radiator construction
A radiator is designed to hold and flow liquid engine coolant and dissipate the heat to airflow created by ram air and airflow created by the radiator fans. Radiators are either downflow, where coolant enters the top tank and exits from the bottom. Or, they’re a crossflow design, where coolant enters from one side and flows horizontally to exit from the other side.
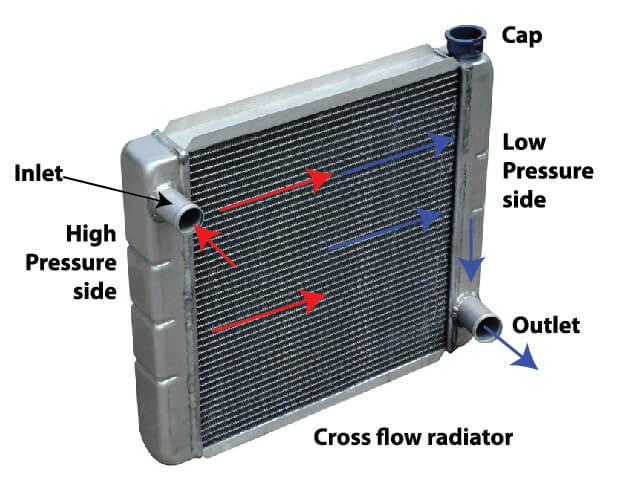
Hot high pressure coolant enters the inlet tank and flows across the tubes to the outlet tank. Airflow across the tubes cools the coolant and lowers both the temperature and pressure. Since the radiator cap is on the outlet tank, high RPMs won’t cause a pressure release
Older style radiators were built with copper tanks and tubes, while modern radiators are build with plastic tanks and aluminum tubes and fins. Aluminum tubes are generally twice the size of the older copper tubes, so they allow for increased heat dissipation.
Radiator cooling
A radiator’s cooling ability is a function of the difference between the radiator’s average core temperature and the temperature of the ambient air temperature, along with the volume of coolant being pumped through the radiator and the amount/speed of the air passing across the tubes and fins.
Intercooler construction
Intercoolers are built with aluminum tanks, tubes, and fins for maximum heat dissipation. The mounting location of the intercooler varies by carmaker. Some carmakers mount the intercooler directly above the intake manifold. In those installations, they fashion air duct from directly behind the grille to flow across the face of the intercooler. In other words, this design relies on ram air to cool the inter cooler. In other designs, the carmaker mounts the intercooler in front of the grille, often in front of or below the AC condenser coil. These designs also rely on fan air or a fan to push air across the intercooler.
©, 2023 Rick Muscoplat
.
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat
