Understanding an Interference Engine: What You Need to Know
Interference Engines Explained: Risks, Benefits, and Maintenance Tips
An interference engine is a specific type of internal combustion engine where the pistons and valves share the same space within the cylinder. In other words, there is a risk that the pistons can come into contact with the valves if the engine’s timing mechanisms fail. This article explores what an interference engine is, how it differs from a non-interference engine, and what vehicle owners should be aware of to avoid potential issues.
What is an Interference Engine?
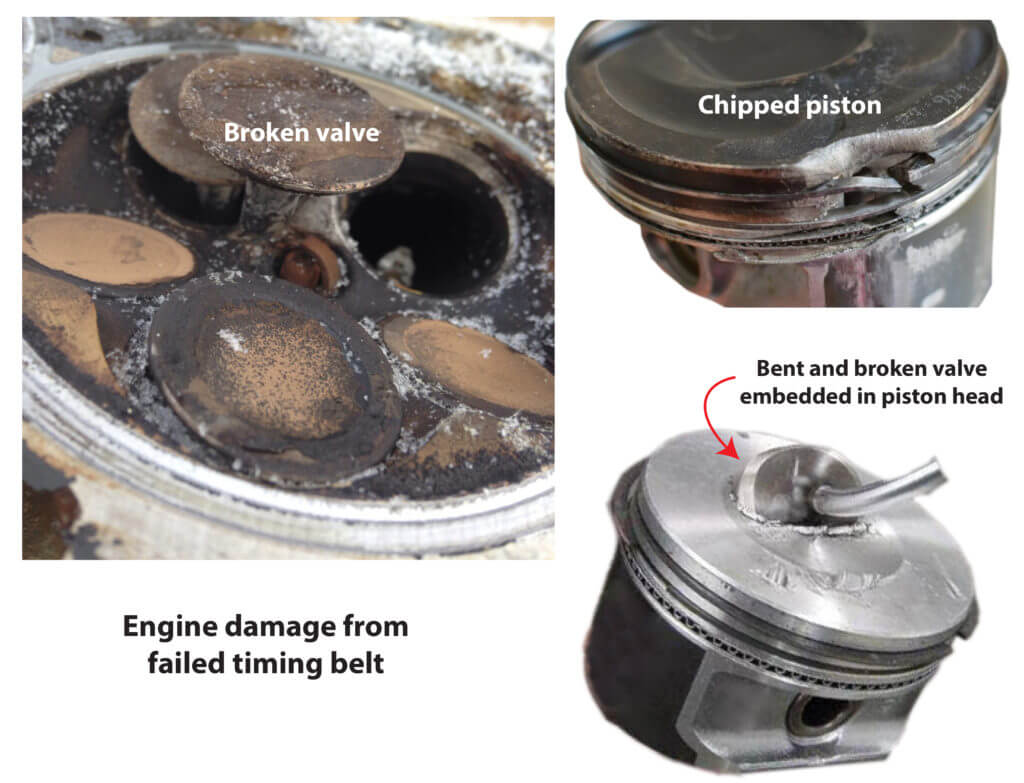
An interference engine is designed so the valves are never open when the piston is at top dead center. The space is maintained by the operation of the timing belt or chain. If the timing belt or chain fails, or if there is an issue with the timing gears or camshaft, the pistons and valves can collide. This collision can bend or break the valves, damage the pistons, and cause serious engine damage.
Interference Engine vs. Non-Interference Engine
The primary difference between an interference versus a non-interference engine is the risk of collision between pistons and valves. In a non-interference engine, a belt or chain failure will not cause valve/piston contact, and the engine won’t be damaged. If the timing belt or chain fails on a non-interference engine, the engine will stop running, but there won’t be any impact damage to the pistons or valve.
In contrast, a timing belt/chain failure will always cause significant damage to an interference engine.
The role of the timing belt or timing chain
The crankshaft and camshaft must rotate in exact sequence with 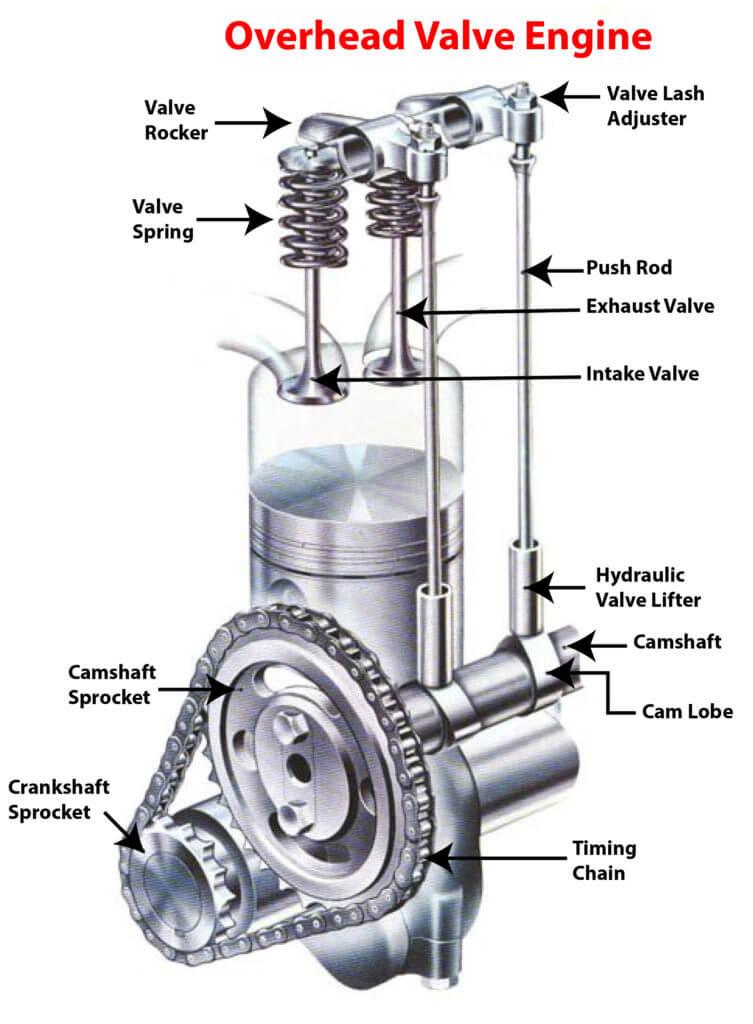 each other. In older push-rod engines, also called overhead-valve (OHV), the camshaft was located in the middle of the engine. Carmakers used either a timing chain or timing gears to like the crankshaft and camshaft. In those engines, the camshaft raised and lowered valve lifters which then moved pushrods to open and close the valves located at the top of the cylinder heads.
each other. In older push-rod engines, also called overhead-valve (OHV), the camshaft was located in the middle of the engine. Carmakers used either a timing chain or timing gears to like the crankshaft and camshaft. In those engines, the camshaft raised and lowered valve lifters which then moved pushrods to open and close the valves located at the top of the cylinder heads.
Pushrod engines lost some efficiencies due to the movement of so many parts. So carmakers switched to overhead cams where the camshaft is mounted above the valves, eliminating push rods entirely. Locating the camshaft above the valves greatly increased the distance between the camshafts and the crankshaft so engineers used a timing belt to move the two rotating shafts.
Advantages and disadvantages of a timing belt
A timing belt is less costly than a timing chain and runs much quieter than a chain. It also doesn’t require lubrication like a chain eliminates the need for a timing belt cover gasket. But unlike a timing chain, timing belts don’t last the life of the engine and must be replaced at regular intervals. The rubber used in timing belts deteriorates over time and can break if not changed at recommended mileage. In an interference engine application, a broken timing belt can result in major engine damage, costing thousands of dollars.
How long does a timing belt last?
That depends on the engine design. On some engines, the timing belt must wrap around multiple idler pulleys which causes higher operating temperatures. Those higher temperatures cause accelerated wear. That’s why some engines require timing belt replacement at 60,000 miles while others require replacement at 120,000 miles. In addition to the design, coolant and oil leaks can cause early belt deterioration and failure.
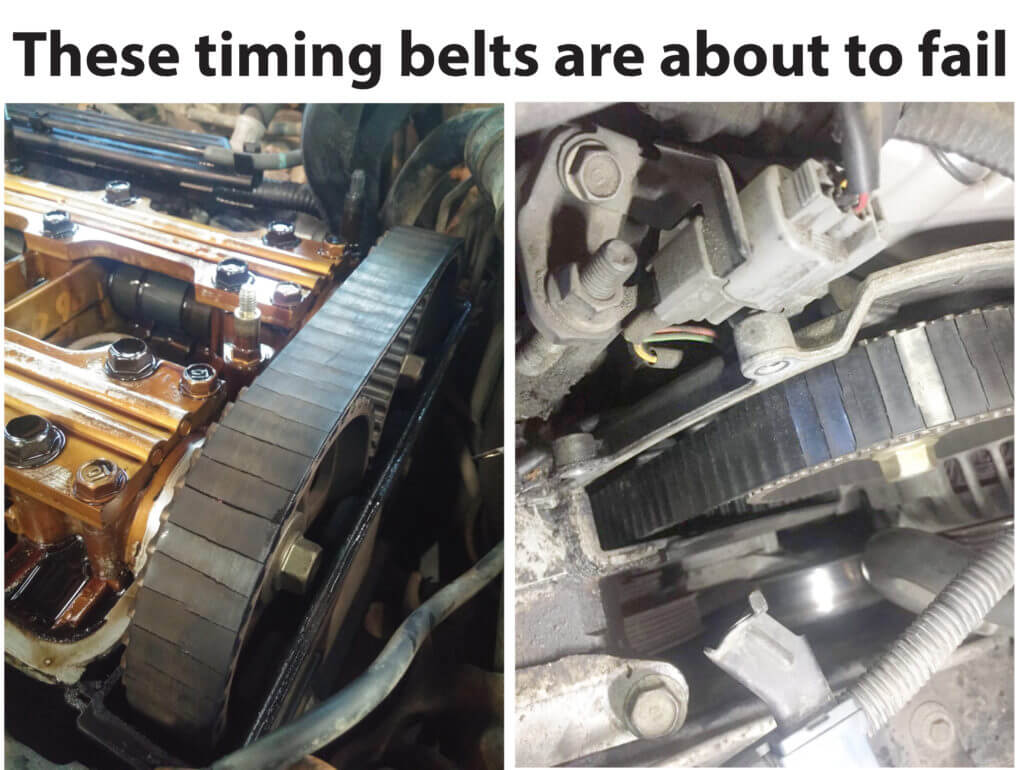
These images show worn out timing belts that could fail and cause major engine damage to an interference engine
Not all timing belt engines are interference designs. If a timing belt fails in a non-interference engine, the engine will die, but mechanical damage will not be incurred.
For more information on when to change your timing belt, see this post
Examples of damage from a failed timing belt

What Vehicle Owners Should Be Aware Of
Regular Timing Belt or Chain Replacement Is Critical
The most important maintenance task for an interference engine is to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for timing belt or chain replacement. Timing belts typically need to be replaced every 60,000 to 100,000 miles, which can vary depending on the vehicle. Timing chains generally last longer but may still require replacement or maintenance. Regularly replacing the timing belt or chain reduces the risk of timing failure and subsequent engine damage.
Be Aware of the Engine Design When Buying a Used Vehicle
If you’re buying a used vehicle, it’s helpful to know whether the engine is an interference or non-interference type. This information can influence your decision and help you understand the maintenance requirements better.
©, 2020 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat
