Ford P0410, Ford P0491
Ford P0410, Ford P0491 — How to diagnose and fix
Ford P0410, Ford P0491 refers to the secondary air system
What is secondary air?
The secondary air system is an emissions control system that’s used during a cold startup to reduce hydrocarbon emissions. Hydrocarbon emissions are very high at cold startup because the PCM commands a rich fuel mixture to start the cold engine. The cold engine tends to quench combustion early, and that unburned fuel flows into the catalytic converter. To burn that extra fuel, the catalytic converter needs more oxygen than it’s getting from cold start exhaust. That’s where the secondary air system comes into play.
The secondary air pump pushes extra air into the exhaust manifold to oxidize the hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide that are in high numbers during a cold start.
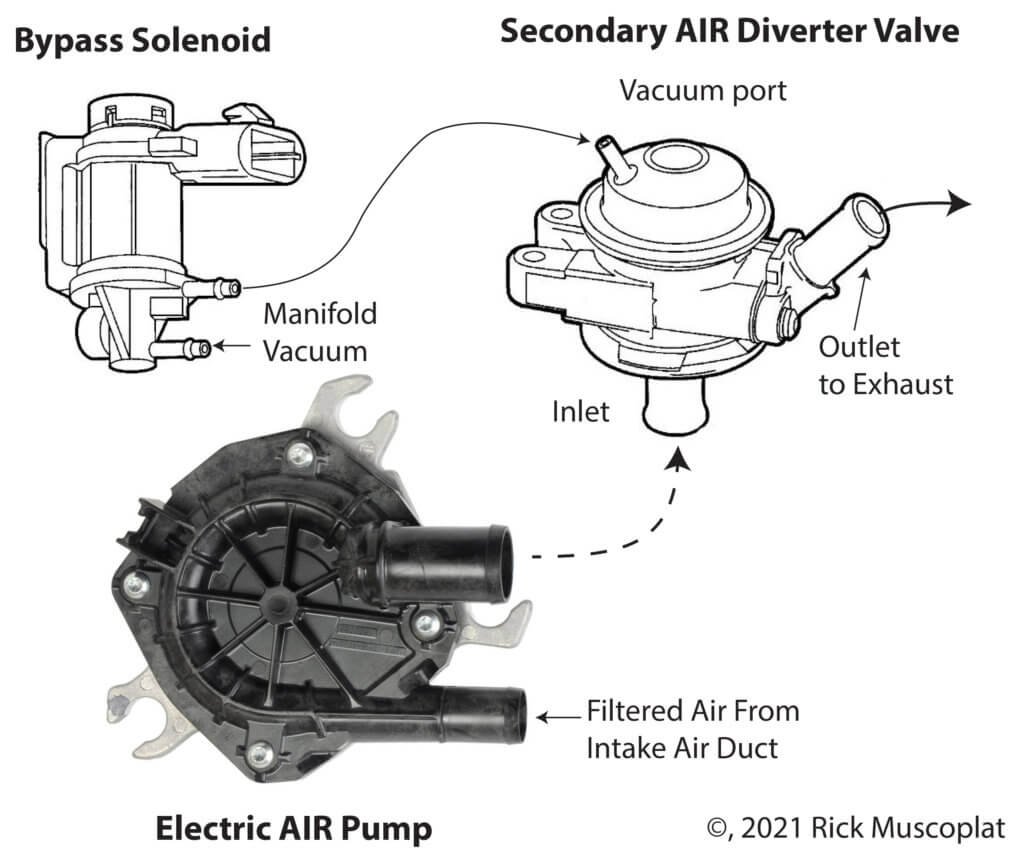
Secondary air components
• Secondary AIR (air injection reaction) pump
• Combination check valve and diverter valve (solenoid operated)
• Connecting hoses, wires and vacuum lines
How the Ford Secondary Air System operates
At startup, the PCM monitors the engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT), cylinder heat temperature (CHT), mass airflow/intake air temperature (MAF/IAT), and the crankshaft position sensor.
If the PCM determines the engine is cold and requires secondary air, it waits 15-seconds after startup and then energizes the AIR relay to start AIR pump and the AIR bypass solenoid. The bypass solenoid opens, allowing manifold vacuum to flow to the secondary air diverter valve. The diverter valve then opens, allowing pressurized air from the AIR pump to flow into the exhaust manifold.
The PCM monitors upstream and downstream oxygen sensors to determine when the catalytic converter has “lit off” (hot enough to burn hydrocarbons). It knows the secondary air system is working when it sees the downstream O2 sensor show a leaner condition
Once the catalytic converter is up to temperature and operating properly, it no longer needs the oxygen in the secondary air. So the PCM removes power from the air pump and the bypass solenoid. Without power, the solenoid defaults to the closed position, cutting off manifold vacuum from the secondary air diverter valve and the valve closes and acts as a check valve to prevent exhaust gasses from back-flowing from he manifold to the pump.
What goes wrong with the Ford Secondary Air System?
The most common trouble codes are Ford P0410, and Ford P0491
P0410 – Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System. The AIR system detected a lack of air flow with the secondary AIR pump ON.
P0491 – Secondary Air Injection (AIR) System Insufficient Flow (Bank 1)
The lack of airflow can be caused by:
• Failed AIR bypass solenoid
• Failed secondary air diverter valve
• Obstruction of airflow in/out of the AIR pump or from the diverter valve to the exhaust manifold
The most common failure point is the secondary air diverter valve.
Test the bypass solenoid and diverter valve
Back-probe the violet/grey wire to the bypass solenoid 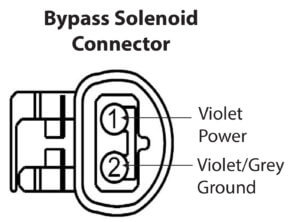 and connect a jumper wire from the violet/grey to a ground point (key in RUN position but engine not running). This grounds the control coil of the AIR relay, closing the contacts and providing power to both the AIR pump and the bypass solenoid. You should hear the electric AIR pump start. If you don’t hear the pump start, check for pump power on the grey/yellow wire and check for good ground on the black/yellow wire.
and connect a jumper wire from the violet/grey to a ground point (key in RUN position but engine not running). This grounds the control coil of the AIR relay, closing the contacts and providing power to both the AIR pump and the bypass solenoid. You should hear the electric AIR pump start. If you don’t hear the pump start, check for pump power on the grey/yellow wire and check for good ground on the black/yellow wire.
If the pump runs, disconnect the jumper wire from ground. Then start the vehicle and reconnect the jumper wire. Disconnect the vacuum line from the secondary air diverter valve and check for manifold vacuum. If you find vacuum, then the problem is in the secondary air diverter valve or an obstruction between the diverter valve and the exhaust manifold.
©, 2021 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick MuscoplatCategories
- Aviator
- C-MAX
- Crown Victoria, Grand Marquis, Lincoln Town Car
- E-Series Vans
- Edge
- Escape, Mariner
- Escort
- Excursion
- Expedition, Navigator
- Explorer
- F-Series Trucks
- Fiesta
- Five Hundred
- Flex
- Focus
- Ford 7.3 Diesel Engine
- Freestar, Montery
- Freestyle
- Fusion Milan
- Mark LT
- Mercury Village
- MKC
- MKS
- MKT
- MKX
- MKZ
- Mountaineer
- Mustang
- Navigator
- Ranger
- Taurus, Sable
- Town Car
- Tracer
- Transit
- Windstar
- Zephyr
