What is a camshaft position sensor?
What is a camshaft position sensor?
The camshaft sensor is an electronic device that’s mounted near a notched wheel on the e camshaft. The notched wheel has a series of equally spaced teeth and one or two gaps in the spacing. The camshaft sensor detects the exact position of the camshaft by counting the number of notches from the gap. The ECM uses that information along with the information from the crankshaft position sensor to determine when to fire the spark plugs and fuel injectors.There are two types of camshaft position sensors; variable reluctance and hall effect.
Variable reluctance (VR) camshaft sensor

Camshaft position sensor
This type of camshaft sensor uses a transducer to detect the presence of ferrous objects passing near the sensor. The VR sensor has a magnet wrapped in a coil of wire. It is mounted in a stationary position at a set gap away from a rotating ferrous notched ring. As the teeth on the rotating notched ring pass by the sensor, the teeth on the notched ring cause a rising/falling amount of magnetic flux past the magnet.
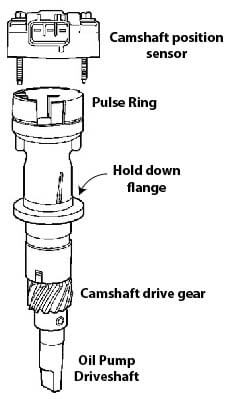
Ford style camshaft sensor sits on top of distributor shaft that is geared to the camshaft. It turns a pulse ring and the pulse is detected by the sensor.
When the tooth is directly in front of the sensor, the magnet flux is at a maximum. As the tooth rotates away from the sensor, the flux drops off. So the scope signal the PCM sees is a typical AC analog sine wave. A VR sensor requires no power to operate.
Hall Effect camshaft sensor
A Hall Effect sensor contains a thin metal strip with a current applied to it. When a magnetic field passes in front of the sensor, the electrons are deflected towards one edge of the metal strip, producing a voltage gradient across the short-side of the strip (perpendicular to the feed current). The voltage change is detected and translated into a digital signal that’s sent to the PCM to determine fuel injection or spark timing.

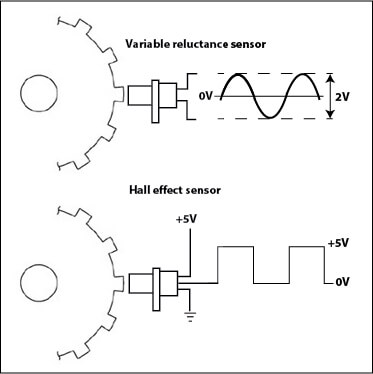
2 types of crankshaft position sensors: Variable reluctance and Hall Effect
The PCM uses input from both the crankshaft position sensor and the camshaft position sensor to determine fuel injector and spark timing.

Ford camshaft synchronizer with alignment tool
What does a camshaft position sensor do?
A camshaft position sensor is used on a fuel injected engine to inform the powertrain control module (PCM) the exact position of the camshaft so the computer can know when to trigger the ignition coil to generate a spark. It takes the place of a distributor in older engines. Some car makers rely on both the camshaft and crankshaft sensors to trigger the fuel injectors and the spark plugs.
Where is the camshaft position sensor located?
The notched wheel can be mounted on the front of the camshaft near the timing belt or on the rear of the camshaft near the former location of the distributor gear. The notched wheel (also called a “reluctor ring” or “tone ring”) has evenly spaced teeth and a timing gap. As the tone ring rotates, the camshaft position sensor senses each notch and reports the movement to the PCM. That’s how the PCM determines the number of degrees of camshaft movement AND the rate of rotation speed of the camshaft. The timing gap helps the computer determine when a full revolution has occurred.
What happens when a camshaft position sensor fails?
A failing sensor can cause a no start, misfire, rough idle, hesitation, vibration, backfires, lack of power or engine stall. Camshaft position sensors are damaged by heat and impact and wiring harness can be damaged by vibration, impact, heat and water intrusion. A camshaft position sensor can fail intermittently causing the poor operation symptoms listed above, or it can fail intermittently when hot but work fine when cold, or vice versa. When it fail totally, you will experience a “crank but no start condition.”
How to test a camshaft position sensor?
A VR type sensor can be tested using a digital voltmeter set to the AC scale. Connect the meter and crank the engine. You should see an AC voltage. However, this only tests the sensor’s ability to generate an AC voltage. The meter can’t measure amplitude and frequency. For that, you need a digital oscilloscope.
A Hall Effect sensor can only be tested with a digital oscilloscope.
Camshaft position sensor replacement cost
Crankshaft sensors usually cost less than $100 and the labor to replace the sensor usually is less than one-half hour. However, the cost to diagnose the failure can easily run upwards of $150, making the total repair cost around $300-$400.
©, 2018 Rick Muscoplat
