Troubleshoot HID headlights — step by step process
Learn how to troubleshoot HID headlights and fix them yourself
Before you can troubleshoot HID headlights, you have to understand how each component works. This is just a summary. If you want a more in-depth understanding, see this post. First, understand how HID headlights work
HID HEADLIGHT COMPONENTS
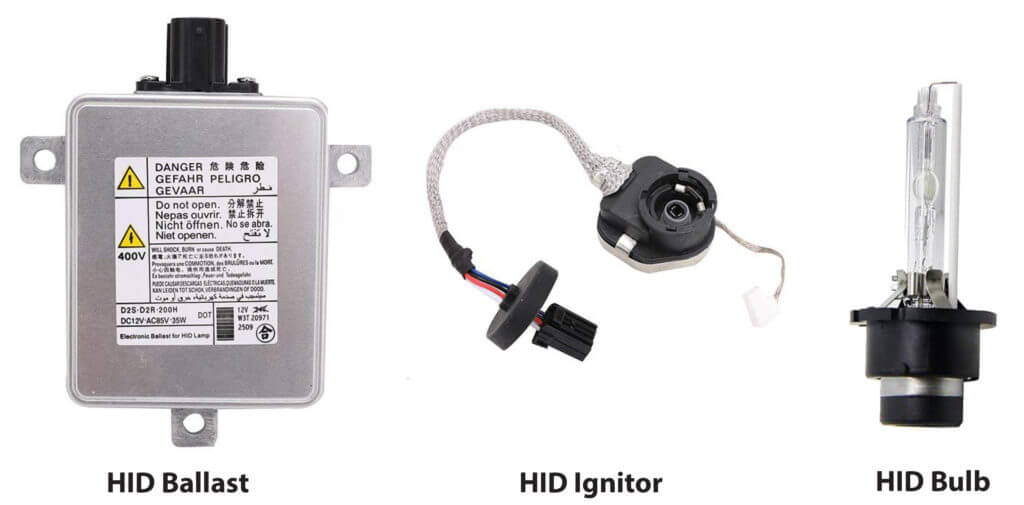

HID BULB

Troubleshoot HID headlights by swapping in a known good bulb
An HID bulb consists of outer shell made from cerium-doped quartz. The outer shell houses the inner bulb or “arc tube.” The inner quartz envelope is made from fused quartz with two tungsten electrodes. The material is special quartz that can withstand the high arc temperature, which burns at up to 1,500°F.
When a powerful current is applied to the electrodes, it lights an arc forming two bright or “hot” spots, one near each electrode. The arc is ionized gas that produces a plasma discharge that generates high intensity light. In many ways, HID bulbs are just like fluorescent or neon light, which an electrode at each end and glowing gas that produces light once the arc is lit.
To learn more about HID headlight bulb terminology, read this post
HID BALLAST
The ballast’s job is to regulate power to the HID bulb to maintain the arc. It must provide a constant 35 watts at 70 to 110 volts. The HID igniter starts the arc with very high voltage, but the ballast is what maintains the arc.
HID IGNITER

An HID Igniter boosts ballast voltage up to 15,000- 25,000 volts
The HID igniter boosts voltage coming from the ballast to around 15,000 to 25,000 volts; enough power to jump the air gap between the two electrodes and “light” the arc. Once the arc is “lit,” the ballast maintains the arc.
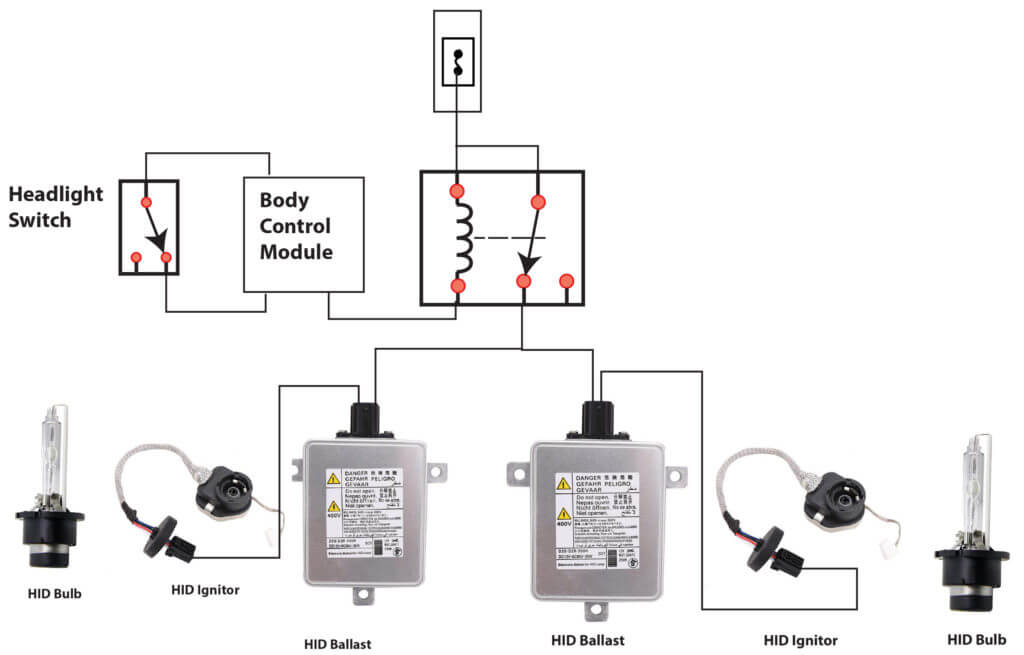
Typical wiring diagram of an HID headlight system. Use this diagram to start the process when you troubleshoot HID headlights
First, check for power to the ballast
Headlight power can be switched from the headlight switch (in older vehicles), a headlight relay, or from the body control module.
So your first step is to check for power to the ballast. If the ballast isn’t getting power and ground, it can’t run the headlights.
Next check the bulb
Signs of a bad HID headlight bulb
• HID headlight bulb flickering is the EARLIEST sign of bulb failure.
• HID headlight bulb shuts off after being on for a while. Shut off is sporadic and unpredictable but happens more and more often over the next 100 hours of operation. However, shutting off can also be caused by a bad ballast. Swapping in a known good bulb helps confirm or deny a bad ballast.
• HID headlight bulb gives off a dim pink glow
Swap the problem bulb to the opposite side. If it works there without shutting off, the problem is in the ballast. It’s failing to maintain constant power to the bulb
A worn bulb tends to lose its arc, so the ballast tries to relight it. The ballast will make multiple attempts to re-light the bulb until the ballast overheats and shuts down. If your HID bulb shuts off sporadically and unpredictably; maybe just once in a 24-hr period, try this.
Turn on the HID headlights and wait for the bulb to shut off by itself. Then turn off your headlight switch and immediately turn it back on. This resets the ballast. If the bulb lights with a weak pink/purple color, it’s usually a bad bulb.
If your HID bulb shows any of the above symptoms after swapping to the opposite side, replace the bulb.
HID ballast diagnostic tip
An HID ballast is a boosting transformer that converts battery voltage  into the approximately 75 to 110 volts needed to maintain the arc.
into the approximately 75 to 110 volts needed to maintain the arc.
The ballast is designed to detect bulb shut down. If the bulb turns off, the ballast will automatically restart the bulb within ½ second. This happens so quickly you may not even notice that it shut off in the first place.
However, as the bulb ages, it may shut off (drop its arc) more often. That can happen as many as 30 times per minute. When that occurs, the ballast tends to overheat. To protect itself, the ballast itself will shut down. It will not reset itself. The ballast can only be reset by turning the headlight switch off and then on again. However, allow a few minutes cooling time between attempts to allow the ballast to cool down. If you have to repeatedly reset the ballast that’s often a sign of a bad HID bulb.
HID ballast diagnostic tip
Turn on your HID headlights. If both lights are lit, wait for one bulb to turn off. If one doesn’t light when you turn on the headlights, proceed with this test:
Have a helper watch the HID bulb closely as you turn on the headlight switch. They’re looking for any sign of flicker. If there’s no sign of lighting, it’s usually a bad ballast or igniter.
If the HID bulb won’t light on one side
If you’ve swapped the bulb to the opposite side and it lights and stays lit on that side, then the most common cause is a faulty igniter.
Replace an HID bulb
HID systems have very high voltages. Always disconnect the connector to the ballast before disconnecting the wire to the igniter or HID bulb.
Differences between HID bulbs
There are four basic types of HID bulbs: D1, D2a, S and R
D1 series bulbs have a built in igniter. D2 series bulbs do not
An “R” HID bulb is designed to fit in a traditional reflector style headlight assembly. All R HID bulbs have a black painted mask on the glass to shield oncoming drivers from glare.
An “S” HID bulb is designed to fit in a projector-style headlight assembly. It does not have the black mask because projector headlights have a built-in internal shield to prevent glare.
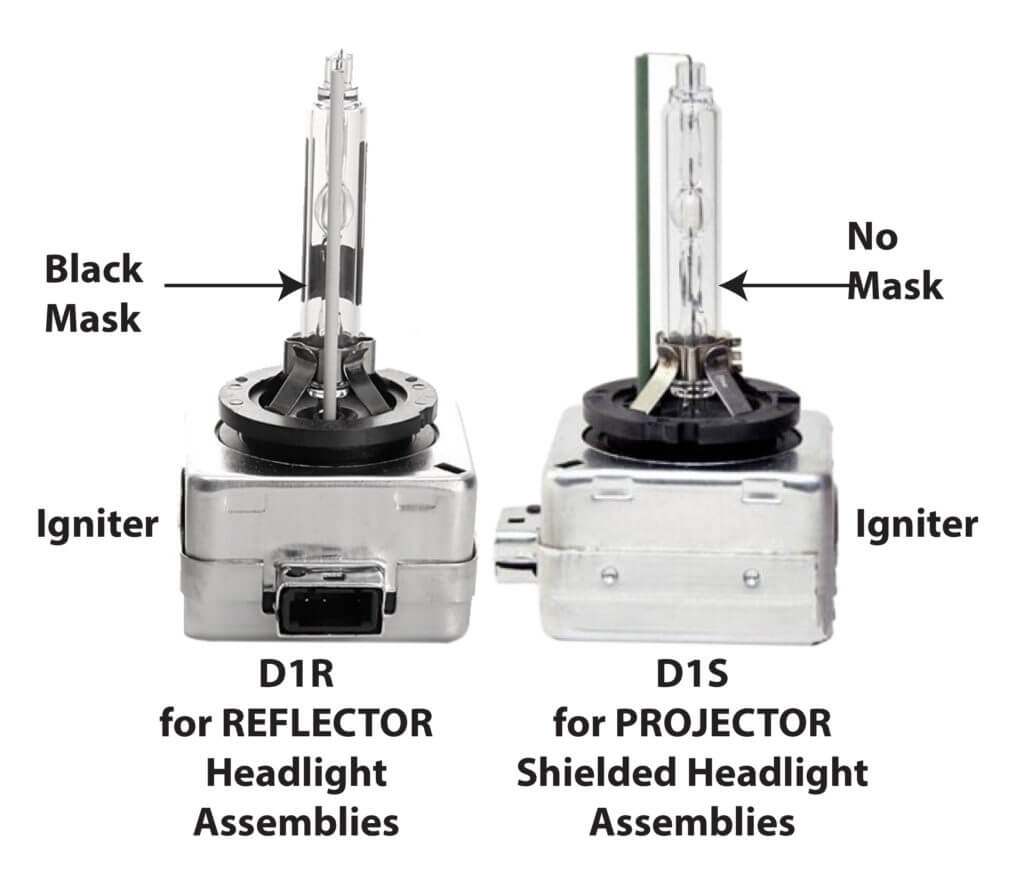

D1R and D1S HID Bulbs incorporate the igniter
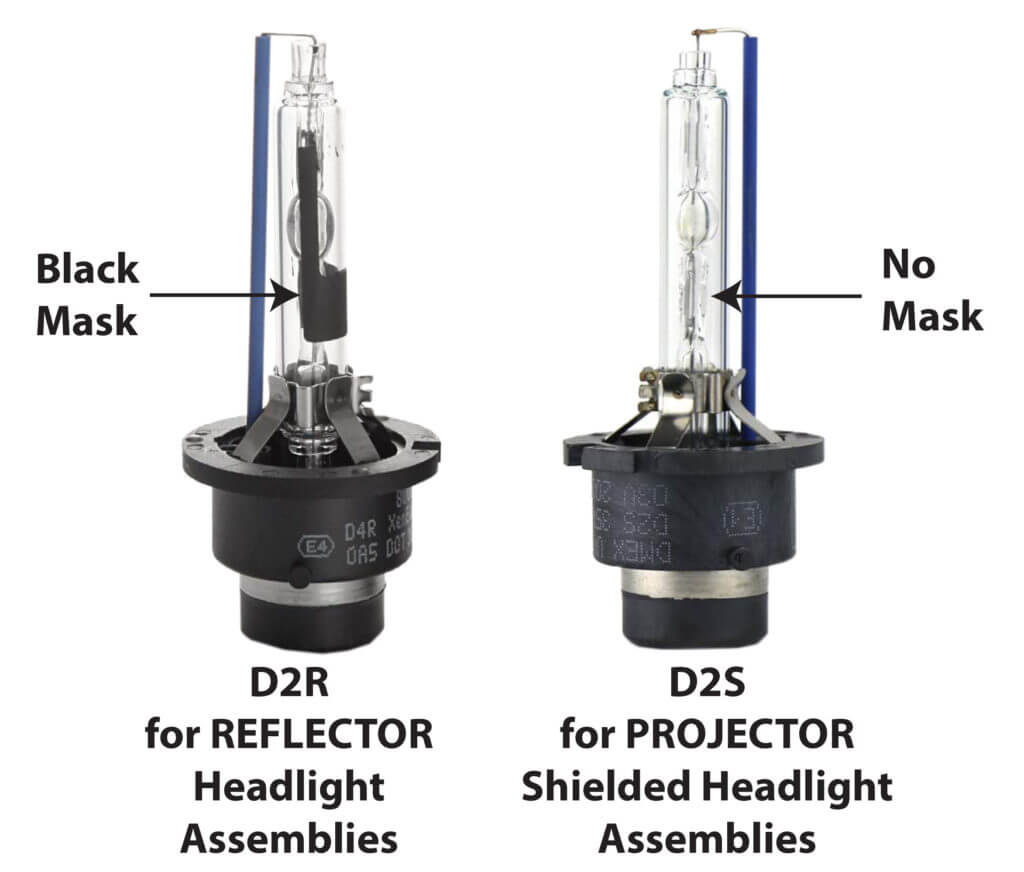

D2R D2S HID bulbs used in HID headlights
Why are High Intensity Discharge headlights are better than halogen headlight bulbs
• 3x more light than halogen bulbs
• 2x more light spread on the road than halogen bulbs
• HID headlights use 2/3 less power than halogen bulbs
• HID bulbs last 3x longer than halogen bulbs
• HID bulbs produce visible and ultraviolet wavelengths so highway signs and other reflective surfaces glow.
©, 2018 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat