Understanding How A Turbocharger Works
How A Turbocharger Works To Increase Engine Efficiency and Power
A turbocharger is a device that increases the efficiency and power output of an internal combustion engine by forcing extra air into the combustion chamber. If you own a vehicle with a turbocharged engine, it helps to understand how a turbocharger works.
A turbocharger consists of two main components: a turbine and a compressor, which are connected by a common shaft.

Turbine: The turbine is driven by the engine’s exhaust gases. As these hot gases pass through the turbine housing, they cause the turbine wheel to spin.
Compressor: The compressor, located on the other end of the shaft, draws in ambient air and compresses it before sending it into the engine’s intake manifold. This compressed air, being denser, contains more oxygen molecules, allowing the engine to burn more fuel during combustion.
How a turbocharger works
The turbocharger is powered by the exhaust gases produced by the engine. As the engine burns fuel and air, it generates hot exhaust gases, which are expelled through the exhaust manifold. These gases are directed into the turbine housing of the turbocharger.
The exhaust gases pass through the turbine housing and spin the turbine wheel. The turbine wheel is connected to a shaft that runs through the center housing to the compressor wheel on the opposite side. As the turbine wheel spins, it transfers energy to the shaft, causing the compressor wheel to spin.
The compressor wheel, located in the compressor housing, draws in ambient air through the engine air intake system. As the compressor wheel spins at high speeds, it compresses the air, increasing its density. This compressed air is then forced into the engine’s intake manifold, where it mixes with fuel and enters the combustion chamber.
The compressed air supplied by the turbocharger contains more oxygen molecules than the naturally aspirated air. This allows the engine to add and burn more fuel in each combustion cycle, resulting in a more powerful explosion and increased power output. The engine can, therefore, produce more power without increasing its size.
Some turbochargers include an intercooler
In many turbocharged systems, an intercooler cools the compressed air before it enters the engine. Compressing air increases its temperature, and cooler air is denser and more efficient for combustion. The intercooler helps reduce the air temperature, further enhancing the engine’s performance and efficiency.
The job of the wastegate and boost control
A wastegate is a valve that controls the amount of exhaust gases flowing into the turbine. It prevents the turbocharger from producing too much boost pressure, which could damage the engine. When the boost pressure reaches a predetermined level, the wastegate opens to divert some exhaust gases away from the turbine, regulating the turbocharger’s speed and maintaining safe boost levels.
Where is the turbocharger located?
The turbo is always located on the exhaust manifold. Some V-6 and V-8 engines have two turbos, one on each bank.
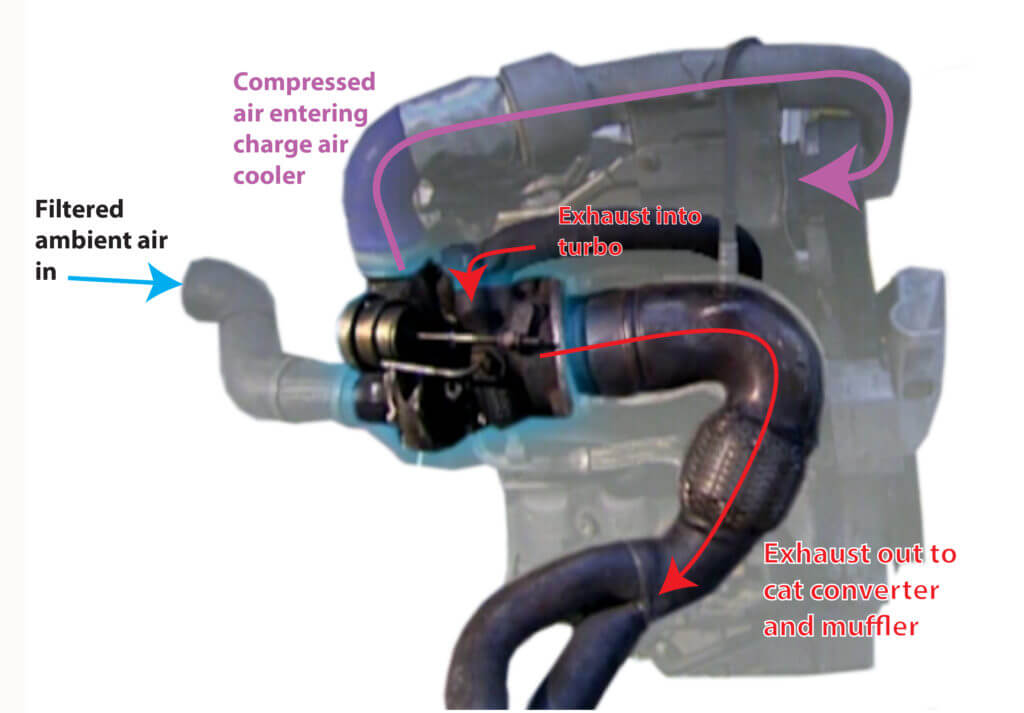
Turbocharger is located on the exhaust manifold
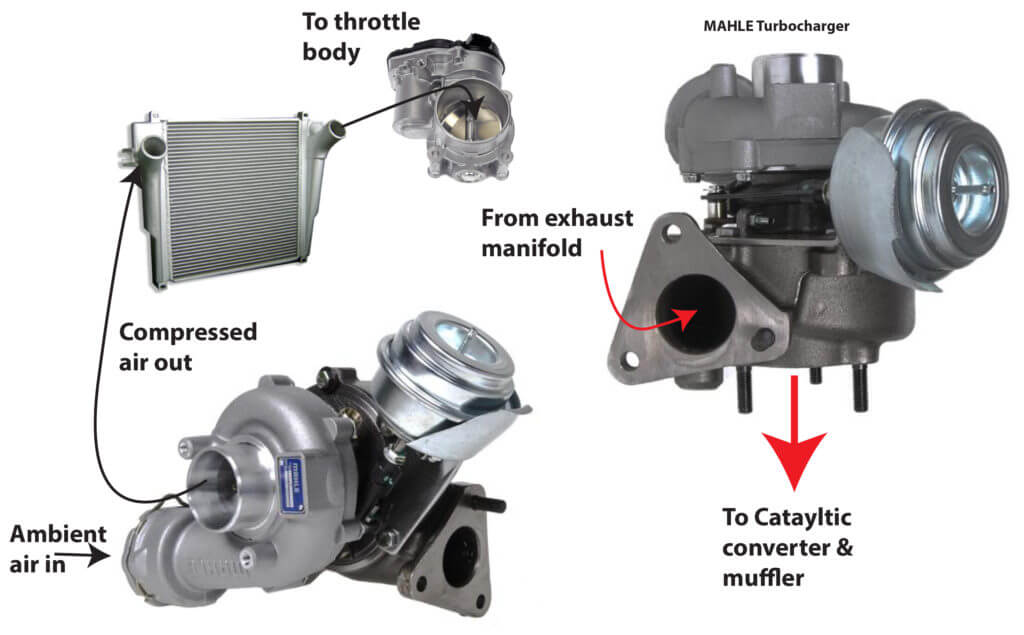
Turbocharger airflow pattern
To learn more about the symptoms of a failing turbo, see this post
To learn what causes turbos to fail, see this post
©, 2018 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat
