Turbo failure
What causes turbo failure?
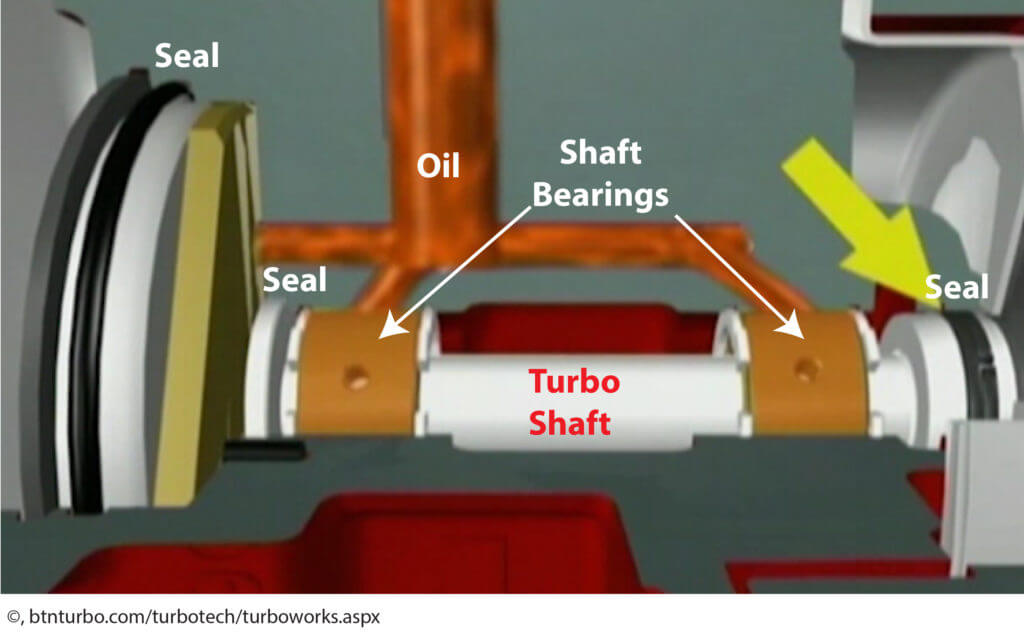
Turbo failure is most often caused by oil starvation, oil contamination, or foreign object damage. Consider this; at highway speeds a turbocharger can spin at rates up to 240,000 RPM, while at wide open throttle, a turbo can spin at up to 360,000 RPM. The only way to prevent the shaft, bearings and seals from disintegrating is to keep a constant flow of cooled oil circulating through the unit.
Turbo failure is most often caused by oil contamination or oil starvation
In fact, according to btnturbo.com, a major rebuilder of replacement turbochargers, 95% of all turbocharger failures are due to oil or foreign object damage, not to manufacturing defects.
What causes turbo oil starvation?
Using the wrong viscosity oil
Think you can solve an oil burning problem by using a high viscosity oil? Well, it won’t work. But worse yet, the higher viscosity oil will cause higher friction in the turbo, which results in higher heat and oil breakdown….which, of course, results in turbo failure. Nice going, Jack.
Running low on oil
Not checking oil levels and topping off between oil changes. All engines use some oil. With synthetic oil and longer oil change intervals, it’s not uncommon to run low between changes. If you don’t check the dipstick and add oil. you can starve the turbo of cooled oil.
Using a poor quality oil filter
Turbo engines generate a lot of heat and that degrades oil,

This is what sludge looks like on an oil filter
even synthetic oil. If you go too long between oil changes or use an economy filter that’s not rated for extended oil change intervals, the oil filter media can become loaded and go into bypass mode. When an oil filter is in bypass mode, the oil BYPASSES the filtering media. In other words, you’re circulating dirty oil through the engine and turbo.
Malfunctioning oil bypass valve—The oil bypass valve can be located in the oil filter or in the oil pump. If it sticks in bypass mode, the oil won’t be filtered.
Clogged oil lines
Oil deposits and sludge can restrict the flow

Clogged oil lines
of oil through the oil cooling lines to and from the turbo. In fact, most rebuilt turbo manufacturers require the installation of new oil lines to the turbo to keep the warranty in force.
Worn oil pump or bearings
An oil pump must deliver oil at a certain pressure and quantity. But pressure and quantity also depend on oil clearances at the bearings. If you’ve neglected oil changes and have worn bearings, the oil will pour out of the bearing clearances, preventing the pump from maintaining proper pressure.
What causes oil contamination?
Going beyond recommended oil change intervals—When oil is used past it useful life, the additives are depleted. So you lose lubricating quality, all anti-wear and anti-corrosion protection.
Overheating
Most turbo engines are equipped with an oil cooler.  The cooler’s job is to remove heat from the oil. Oil coolers can remove heat using an air exchange radiator or a coolant radiator. An air cooled oil cooler usually sits in the front of the vehicle near the radiator. Clogged fins can prevent proper airflow and impact damage can restrict oil flow. A coolant exchange oil cooler circulates engine coolant through a copper tube that’s immersed in the turbo oil flow. Since engine coolant is at a lower temperature than oil coming from the turbo, it cools the oil.
The cooler’s job is to remove heat from the oil. Oil coolers can remove heat using an air exchange radiator or a coolant radiator. An air cooled oil cooler usually sits in the front of the vehicle near the radiator. Clogged fins can prevent proper airflow and impact damage can restrict oil flow. A coolant exchange oil cooler circulates engine coolant through a copper tube that’s immersed in the turbo oil flow. Since engine coolant is at a lower temperature than oil coming from the turbo, it cools the oil.
Gasket leaks
A head gasket leak can allow coolant to enter the oil, which destroys its lubricating abilities.
What causes turbo impact damage?
A clogged air filter, leak in the air duct from the air filter box to the charge

Damaged air compressor turbine
air cooler or from the charge air cooler to the throttle body can introduce road grit or debris into the air compressor turbine. Since the turbine spins at extremely high speeds, ANY debris can destroy the turbine blades.
You can introduce foreign objects into the intake airflow stream any time you check the air filter or disconnect the air duct. A rag, loose screws or nuts can instantly destroy a turbo.
Over-revving
Turbos are designed to handle a range of speeds. But if you exceed those speeds, the turbine blades can come apart or the bearing may not be able to handle the load.

Turbine damage from over speed
©, 2018 Rick Muscoplat
Posted on by Rick Muscoplat
